Describe What Surface Tension Is Using Kinetic-molecular Theory
Taking them as centers and molecular range as radius a sphere of influence is drawn around them. Surface tension is defined as the force per unit length acting perpendicular on an imaginary line drawn on the liquid surface tending to pull the surface apart along the line.

Chapter 10 Notes The Kinetic Molecular Theory Is Based On
The kinetic molecular theory can be used to explain the results Graham obtained when he studied the diffusion and effusion of gases.
. Therefore net force acting on P is zero. If F is the force acting on the length l of the line AB then surface tension is given by TFl. This in turn determines whether the substance exists in the solid liquid or gaseous state.
Surface tension is determined by two thermodynamic relationshipsthe adsorption isotherm that relates the bulk concentration to the surface concentration of the surfactant and the surface equation of state that relates the surface tension to the amount of surfactant adsorbed. Surface tension resists penetration of objects into a liquid. 4What does the negative slope of waters solidliquid equilibrium line indicate.
Through the use of KMT a few different laws have been created to help quantify the relationship between the. Describe Kinetic Molecular Theory. Consider two molecules P and Q as shown in Figure.
V 1 T 1 V 2 T 2 V 1 T 1 V 2 T 2. The Kinetic Molecular Theory and Grahams Laws. Along the surface the particles are pulled toward the rest of the liquid as shown in the picture to the right.
But on surface there are no molecules on top to balance the downward force. Consider 3 molecules of a liquid. This property of the liquid surface is known as surface tension.
This can be written as. The cohesive forces on the liquid molecules within the surface film differ from those functioning on molecules deep within the interior of the liquid. The forces on a molecule are balanced out by forces exerted by other molecules around the given molecule.
Gamma F d. Explanation of Formation of Drops and Bubbles. The force is perpendicular to the line and tangential to the liquid surface.
Using the kinetic molecular theory explain why a gas can be easily compressed while a liquid and a solid cannot. Capillarity and Capillary Action. The development of surface tension arises because of the cohesive forces acting between the molecules of a liquid.
Why iscarbon dioxides positive. Surface Tension and Surface Energy. Surface tension is the energy required to increase the surface area of a liquid by a unit amount and varies greatly from liquid to liquid based on the nature of the intermolecular forces eg water with hydrogen bonds has a surface tension of 729 x 10-2 Jm 2 at 20C while mercury with metallic bonds has as surface tension that is 15 times higher.
Describe Kinetic Molecular Theory. Charles Law states that at constant pressure the volume of a gas increases or decreases by the same factor as its temperature. All particles have energy but the energy varies depending on the temperature the sample of matter is in.
Surface tension denoted with the Greek variable gamma is defined as the ratio of the surface force F to the length d along which the force acts. This is known as the surface tension. The Kinetic Molecular Theory KMT is a model based on a series of postulates that explain the behavior of matter.
This article is devoted to the description of surface tension and physical adsorption in pure liquids and solutions from the molecular standpoint. Excess Pressure Across the Free Surface of a Liquid. The Kinetic-Molecular Theory Explains the Behavior of Gases Part I.
Assume the case in which a gas molecule represented by a sphere is in a box length L Figure 1Through using the assumptions laid out above and considering the sphere is only moving in the x-direction we can examine the. It tries to contract and have a minimum surface area. Surface tension a force that tends to pull adjacent parts of a liquids surface together thereby decreasing surface area to the smallest possible size capillary action.
Why is carbon dioxides positive. Effect of Impurity and Temperature on Surface Tension. Every Liquid when taken in a container has the property that its free surface behaves like a stretched membrane with a tendency to contract and acquire the minimum surface area.
Surface Tension with molecular theory class 11 physics. 4- Liquids exhibit surface tension a force that tends to pull adjacent parts of a liquids surface together thereby decreasing the surface area to its smallest possible size. How do molecular forces affect surface tension.
Matter is made up of particles that are constantly moving. 486 x 10-1 Jm 2. These relationships are influenced by intermolecular interactions among the hydrocarbon chains.
The kinetic molecular theory of matter states that. Molecular Theory of Surface Tension. Kinetic Molecular Theory and Gas Laws.
A molecule A well within the liquid and molecules B and C lying at within the. Explore KMT including its postulates and learn about the properties of solids. It is based upon the methods of thermodynamics and statistical mechanics.
4What does the negative slope of waters solidliquid equilibrium line indicate. The macroscopic phenomena of pressure can be explained in terms of the kinetic molecular theory of gases. The molecule P is attracted in all directions equally by neighboring molecules.
This property of liquid is called surface tension. Recalling that gas pressure is exerted by rapidly moving gas molecules and depends directly on the number of molecules hitting a unit area of the wall per unit of time we see that the KMT conceptually explains the behavior of a gas as follows. Therefore a force perpendicular to the surface of water creates a thin elastic film.
5- Liquids have capillary action the attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid. The surface of a liquid at rest behaves like a stretched membrane. Using the kinetic molecular theory explain why a gas can be easily compressed while a liquid and a solid cannot.
Surface tension has the dimension of force per unit length. The key to this explanation is the last postulate of the kinetic theory which assumes that the temperature of a system is proportional to the average kinetic energy. Pressure and KMT.
How do molecular forces affect surface tension. According to Kinetic Molecular Theory an increase in temperature will increase the average kinetic energy of the molecules. Molecular Theory of Surface Tension.
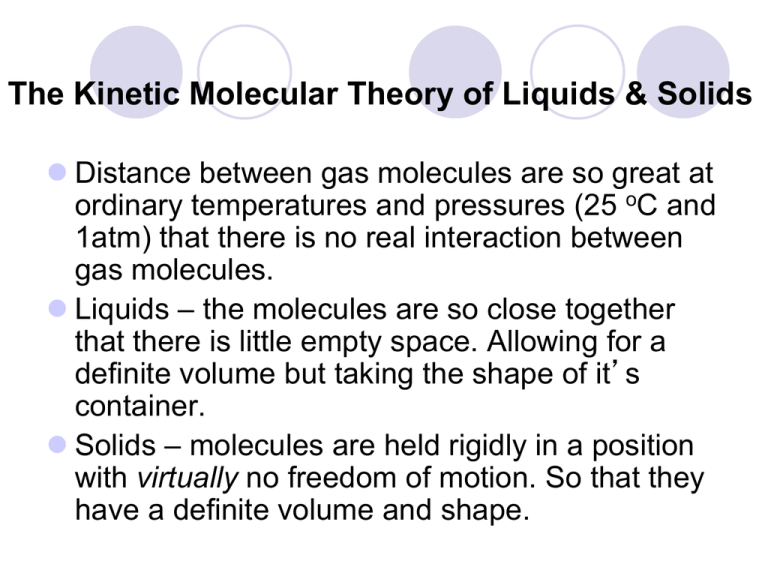
The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Liquids Solids

The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Liquids Solids

The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Liquids Solids Ppt Video Online Download
No comments for "Describe What Surface Tension Is Using Kinetic-molecular Theory"
Post a Comment